Mendel's and his Experiments
Mendel's and his Experiments: Overview
In this topic, we will discuss Mendel's experiments. It highlights Mendel's law of inheritance here. We will come across the two modern applications of genetics as well. We will also be introduced to the term heredity.
Important Questions on Mendel's and his Experiments
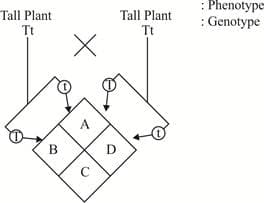
Look at the given diagram and answer the following question :
Identify the phenotypic ratio of A, B, C, D.
A homozygous tall pea plant with yellow seeds is crossed with a dwarf pea plant with green seeds. The phenotypic ratio of its F2 plants is 9:3:3:1. It is representing:
If a homozygous tall plant is crossed with homozygous dwarf plant, the offspring will be
If a pure tall plant is crossed with a dwarf plant, the offspring will be
A typical phenotypic monohybrid ratio of F2 in Mendel's experiment is
If tall (T) is dominant over dwarf (t) and round seeds (R) is dominant over wrinkled seeds (r). If the genotype is ttRr the phenotype would be
A gamete contains
Which of the following terms represent two form of a trait on chromosomes.
When Aa hybrid is crossed back with the homozygous dominant parent, the phenotypic ratio of the progeny will be
In a pea plant, the gene 'T' for tallness is dominant over the gene 't' for dwarfness. If two heterozygous individuals are crossed
If a homozygous tall pea plant is crossed with another homozygous tall pea plant, the progeny in the F1 generation will be :
Which of the following character was not a part of Mendel's experiments?
The following characters are observed in different pea plants :
A) Seeds round, flowers white, flowers in axial position.
B) Pods inflated, seeds wrinkled, pods green.
C) Seeds green, pods constricted, flowers violet.
D) Flowers white, pods yellow, flower position terminal.
How many characters are dominant and recessive in each plant mentioned above according to the studies of G.J. Mendel respectively?
The correct answer is :
A Rh+ve man (heterozygous) is married a Rh-ve lady. They had four children, only first and the last are Rh+ve. Then the child with erythroblastosis foetalis / HDNB among the four children probably is
The number of offspring produced in F2 generation of dihybrid cross is 1600. Find the number of F2 offsprings with double dominant phenotype?
In monohybrid cross, the proportion of explains
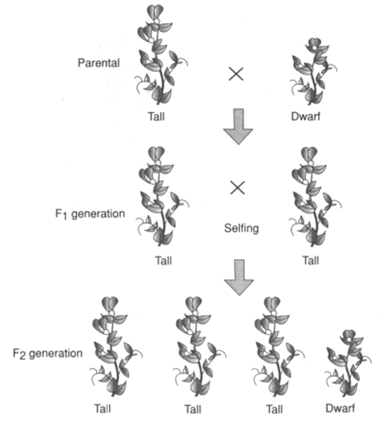
The below diagram shows:
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, how many of progeny in generation possess genotype rryy?
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, how many individuals are heterozygous of both the character in -generation?
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, how many individuals are homozygous recessive for one of the character only in generation?
